Introduction
Cataracts are a common eye condition characterized by the clouding of the lens, leading to diminished vision quality. This condition often develops slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Its impact on an individual’s ability to perform daily activities efficiently makes understanding and managing cataracts crucial. Cataract surgery, a safe and effective treatment, restores vision by replacing the clouded lens with an artificial one. This guide aims to provide a detailed overview of cataracts, their treatment options, and what one can expect from cataract surgery.
What Are Cataracts?
Definition and Causes
A cataract is a clouding of the eye’s natural lens, which lies behind the iris and the pupil. It is primarily associated with aging but can also result from other risk factors such as diabetes, smoking, prolonged exposure to ultraviolet sunlight, and certain genetic predispositions. The lens of the eye is composed of water and protein, arranged in a way that keeps the lens clear and allows light to pass through. However, as we age, some of the protein may clump together and start to cloud a small area of the lens, a process that is the beginning of a cataract.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
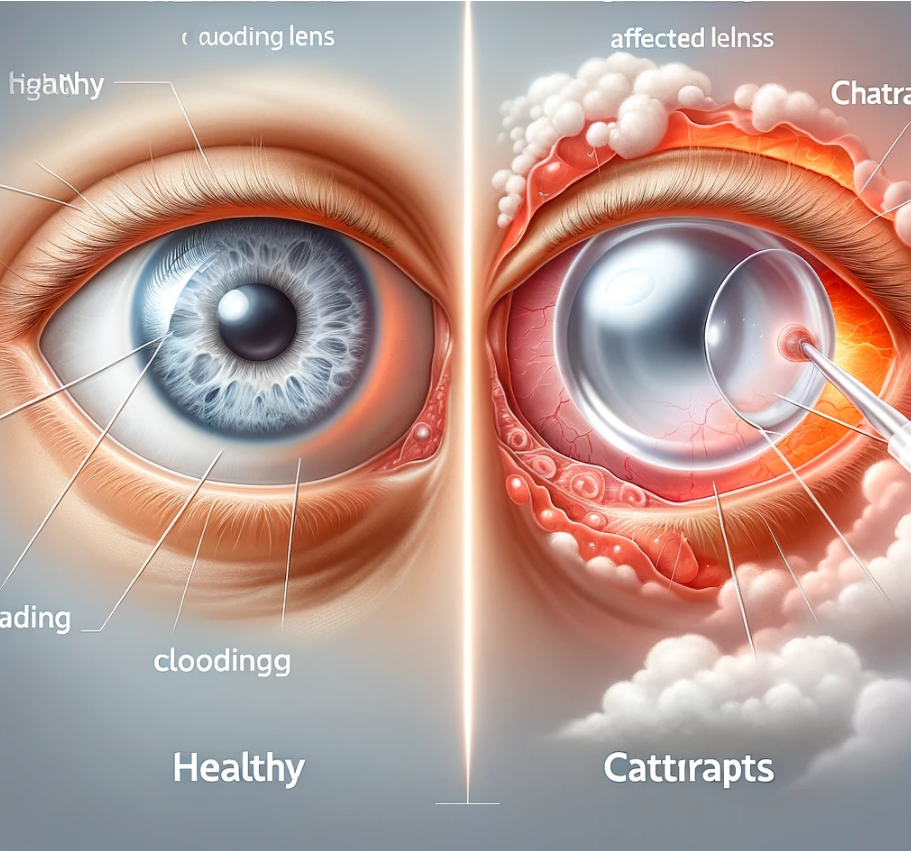
The most common symptoms of cataracts include blurred or dim vision, difficulty with night vision, sensitivity to light and glare, the need for brighter light for reading and other activities, and seeing “halos” around lights. Interestingly, the development of a cataract might initially improve a person’s nearsightedness, a phenomenon known as “second sight,” though this is temporary and will worsen as the cataract develops. Diagnosis involves a comprehensive eye examination that includes visual acuity test, pupil dilation, and possibly other tests to examine the health of the eye.
Cataracts develop for various reasons, including aging, trauma, and exposure to radiation. Aging is the most common cause. Over time, the proteins in the eye’s lens begin to clump together, causing the lens to become cloudy. This cloudiness can interfere with the lens’s ability to focus light on the retina, leading to vision problems.
The condition usually progresses slowly, causing gradual vision impairment. Early on, stronger lighting and eyeglasses can help manage symptoms, but as the cataract grows, surgery might become necessary to restore vision. Cataract surgery is recognized for its high success rate and involves the removal of the clouded lens and, in most cases, its replacement with a clear artificial lens.
Preparing for Cataract Surgery
Before undergoing cataract surgery, several essential steps are taken to ensure the procedure is as successful and safe as possible. Here’s what you need to know:
Consultation and Evaluation
A thorough consultation with your eye doctor is crucial. This appointment is not just about diagnosing cataracts but also about understanding your medical history, any medications you’re currently taking, and discussing any other eye conditions you might have. It’s essential to evaluate and possibly treat other eye issues before cataract surgery to improve the overall outcome.
Choosing the Right Intraocular Lens (IOL)
The selection of the intraocular lens (IOL) is a significant part of the pre-surgery discussion. There are various types of IOLs available, including monofocal (for one distance), multifocal (for multiple distances), and toric lenses (for correcting astigmatism). Your lifestyle, vision goals, and the health of your eyes will influence this choice. The IOL becomes a permanent part of your eye and is designed to improve your vision by focusing light correctly onto your retina.
Pre-Operative Measures
Before the surgery, you may need to undergo several tests, such as a painless ultrasound, to measure your eye’s shape and size. This helps in selecting the appropriate IOL. You’ll also receive instructions regarding eating, drinking, and medication adjustments before the procedure. For example, you might be advised to fast for 12 hours before your surgery and to use antibiotic eye drops one or two days prior to the procedure. It’s also important to arrange for transportation home after the surgery, as you won’t be able to drive yourself.
The Cataract Surgery Procedure
Cataract surgery is typically performed on an outpatient basis and usually takes less than an hour. The procedure involves several key steps:
Phacoemulsification
The most common method for cataract surgery is phacoemulsification. After dilating your pupil and numbing the area around your eye, the surgeon makes a small incision in the eye. A tiny probe is then inserted, which emits ultrasound waves to break up the cloudy lens. These fragments are suctioned out, leaving the lens capsule intact for the IOL.
Lens Implantation
After the natural, clouded lens is removed, the surgeon inserts the IOL into the lens capsule. This lens unfolds within the eye and is positioned to replace the natural lens. The incision made is very small and may not require stitches.
Post-Surgery Care
Immediately following the surgery, you may experience mild discomfort, but significant pain is rare. Your doctor will prescribe eye drops to prevent infection and inflammation and may recommend wearing an eye patch or protective shield for a short period. Vision typically begins to improve within a few days, and colors may appear brighter, given the removal of the yellowed lens.
It’s critical to follow all post-operative instructions from your eye doctor and attend follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing and to adjust your vision correction if needed. Most patients can return to their daily activities shortly after surgery, with complete healing often occurring within eight weeks.
This image illustrates the key steps involved in cataract surgery, from the removal of the clouded lens to the insertion of the intraocular lens.
Cataract surgery has a high success rate and offers a significant improvement in vision for most people. However, like any surgical procedure, it carries risks such as infection, bleeding, and in rare cases, retinal detachment. Discussing these risks with your doctor, alongside the benefits, will help you make an informed decision about the surgery.
Recovery and Aftercare
After cataract surgery, patients usually notice an improvement in their vision within a few days, although it’s normal for vision to be blurry initially as the eye heals and adjusts. The lens removed during surgery is often yellow- or brown-tinted, so colors may appear brighter post-surgery because you are looking through a new, clear lens. It’s crucial to follow your eye doctor’s aftercare instructions closely to ensure a smooth recovery and optimal results.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
- Avoiding Strain: It’s important not to bend over, lift heavy objects, or perform activities that might strain your eyes immediately after surgery. These precautions help prevent complications and support the healing process.
- Eye Drops: Your doctor will prescribe eye drops to prevent infection and reduce inflammation. It’s essential to use these as directed to aid in the healing process.
- Protective Eyewear: You may be asked to wear an eye patch or protective shield, especially at night, to protect the eye as it heals.
- Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments with your eye doctor are critical to monitor your healing and address any concerns promptly.
Long-Term Care and Vision Adjustment
- Healing Time: Complete healing typically occurs within eight weeks. During this period, it’s normal to experience some fluctuations in your vision.
- Vision Correction: Most people will need glasses for certain activities, like reading, after surgery. Your doctor will advise when your eyes have healed enough to be fitted for a final prescription, usually between one and three months post-surgery.
- Dealing with Floaters: Some patients notice floaters after surgery, which usually improve over time. If floaters persist or worsen, you should consult your eye doctor.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can cataract surgery correct vision to 20/20?
While many patients experience significant improvements in their vision, achieving 20/20 vision depends on various factors, including the type of intraocular lens implanted and the presence of other eye conditions. Your eye surgeon can provide more personalized expectations based on your specific situation.
How long does the surgery take?
Cataract surgery is typically quick and efficient, usually completed in an hour or less as an outpatient procedure.
Is cataract surgery painful?
Patients are given numbing medications during the procedure, so they should not feel pain. Some discomfort may be experienced after the anesthesia wears off, but this is generally mild and manageable with over-the-counter pain relievers.
What is the success rate of cataract surgery?
Cataract surgery is one of the most successful and frequently performed surgeries in the United States, with a high success rate. Most patients experience a substantial improvement in vision following the procedure.
Remember, each patient’s recovery experience may vary, and it’s essential to communicate with your healthcare provider about any concerns or unusual symptoms during your recovery.
Conclusion
Grasping the nuances of cataract surgery is pivotal, illuminating a path through the fog of misinformation to clear, actionable understanding. This journey into the world of eye health is not merely academic; it’s a beacon for those navigating the challenges of vision impairment due to cataracts. Emphasizing the procedure’s transformative power stresses the importance of early consultation with eye care professionals. Their expertise can demystify the process, tailor approaches to individual needs, and ultimately, unlock a brighter, more vivid world. If cataracts cloud your horizon, let this encouragement to seek professional guidance be your first step towards a clearer future.